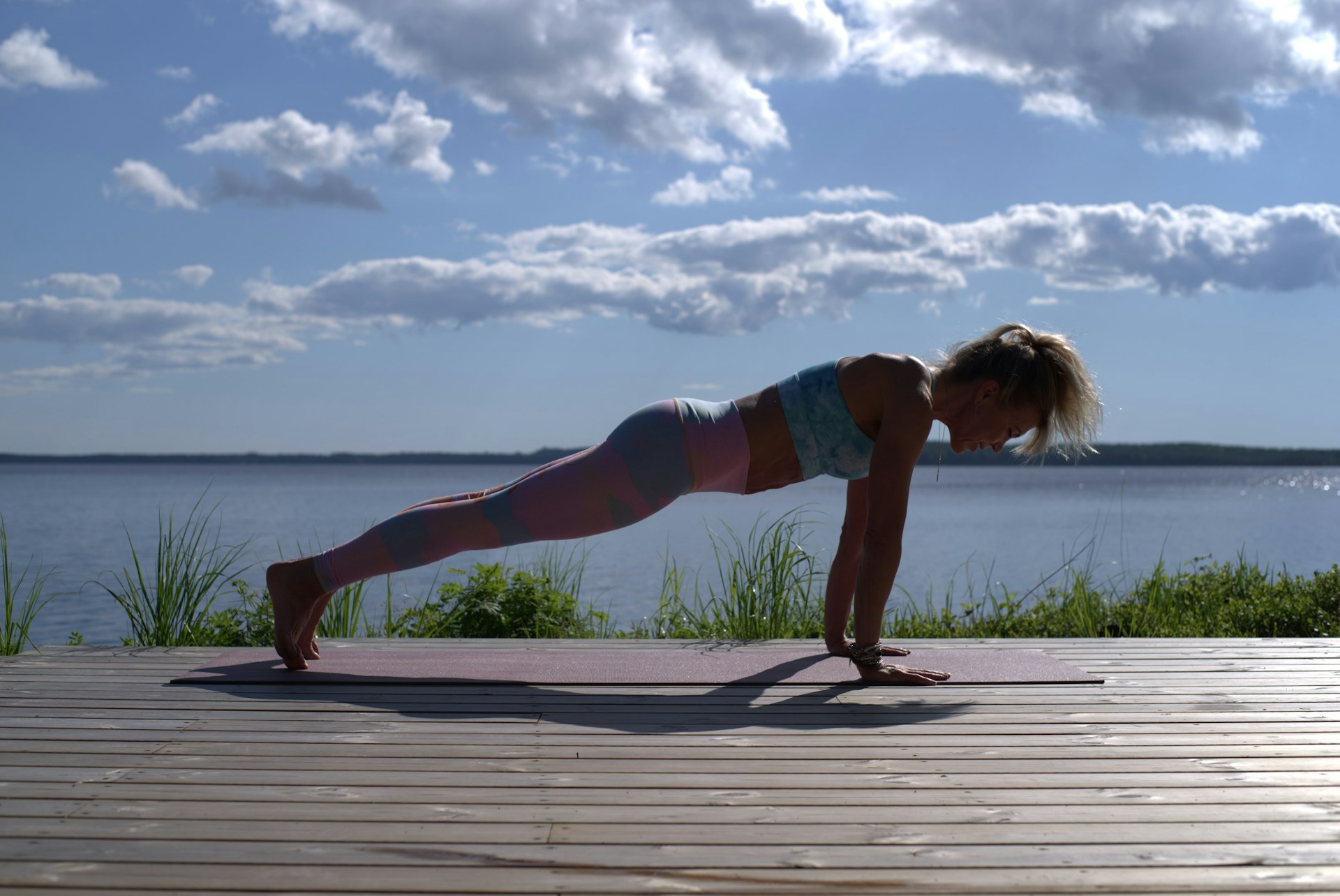
Resistance training is a cornerstone of modern fitness and performance programs. It involves using external loads—such as free weights, machines, resistance bands, or even bodyweight—to stimulate muscle contractions, creating adaptations that improve strength, power, and endurance.
Physical Benefits
Increased Muscle Strength and Hypertrophy
Resistance training causes micro-tears in muscle fibers. When these tears repair, muscles become larger (hypertrophy) and stronger. Studies have shown that progressive overload—the gradual increase of resistance—optimizes muscle growth and increases maximal strength, which is essential for both athletic performance and everyday activities.
Improved Body Composition
By increasing lean muscle mass, resistance training boosts resting metabolic rate, helping the body burn more calories even at rest. As muscle tissue is more metabolically active than fat, a regular resistance training regimen can reduce body fat percentage, improve overall body composition, and enhance physical appearance.
Enhanced Bone Density
The mechanical stress of lifting weights stimulates bone remodeling, leading to increased bone mineral density. This benefit is crucial for reducing the risk of osteoporosis and bone fractures, particularly in aging populations.
Joint Stability and Flexibility
Strengthening the muscles around joints not only enhances overall stability but also helps maintain proper alignment and movement patterns. A well-designed resistance training program can improve joint function and reduce the risk of injuries, making everyday movements easier and more efficient.
Physiological Benefits
Improved Insulin Sensitivity and Metabolic Health
Resistance training has been shown to enhance insulin sensitivity, which aids in better blood sugar regulation. This improvement reduces the risk of metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes. Increased muscle mass contributes to a higher resting metabolic rate, facilitating long-term weight management and metabolic health.
Favorable Hormonal Adaptations
Engaging in resistance training promotes the release of anabolic hormones such as testosterone and growth hormone. These hormones play critical roles in muscle repair and growth, and their increased levels contribute to improved recovery, enhanced muscle synthesis, and overall better physical performance.
Cardiovascular and Vascular Benefits
Although primarily associated with muscle strength, resistance training also positively impacts cardiovascular health. It can lower resting blood pressure and improve blood lipid profiles by increasing high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol. Additionally, resistance training helps improve vascular function, contributing to overall heart health.
Performance Benefits
Enhanced Athletic Performance
For athletes, the improvements in muscle strength, power, and endurance directly translate to better performance in various sports. Increased muscle force production and enhanced neuromuscular coordination boost speed, agility, and explosive power. This is why resistance training is a key component in training regimens for sports such as basketball, soccer, track and field, and many others.
Increased Functional Strength
Resistance training improves the strength needed for daily activities. Whether lifting groceries, moving furniture, or playing with children, stronger muscles lead to better performance in everyday tasks. Enhanced functional strength also contributes to improved posture, balance, and overall quality of life.
Better Movement Efficiency
Through improved muscle coordination and strength, resistance training enhances movement efficiency. This increased efficiency means that less energy is wasted during physical activities, which can lead to improved endurance and faster recovery during both exercise and daily activities.
Psychological and Mental Health Benefits
Boosted Mood and Reduced Stress
Regular resistance training has been linked to lower levels of anxiety and depression. The release of endorphins during exercise can improve mood and reduce stress. Many individuals find that a consistent strength training routine contributes to a more positive outlook and better mental health.
Increased Self-Esteem and Confidence
Achieving strength goals, whether it’s lifting heavier weights or improving body composition, fosters a sense of accomplishment. This progress can lead to enhanced self-esteem and confidence, both in the gym and in daily life.
Improved Cognitive Function
Emerging research suggests that resistance training may benefit cognitive functions, such as memory and executive function. The increased blood flow to the brain and hormonal changes associated with strength training might help improve mental sharpness and reduce age-related cognitive decline.
Injury Prevention and Rehabilitation
Strengthening Muscles, Tendons, and Ligaments
By enhancing the strength of muscles, tendons, and ligaments, resistance training plays a vital role in injury prevention. Stronger muscles can better absorb and dissipate forces during dynamic movements, reducing the risk of strains, sprains, and other injuries.
Correcting Imbalances and Improving Stability
A balanced resistance training program can address muscular imbalances that might lead to injuries. By focusing on both the agonist and antagonist muscles, as well as core stability, resistance training improves overall movement mechanics and joint alignment, which are essential for both athletic performance and injury prevention.
Effective Rehabilitation
Resistance training is a common component of rehabilitation programs. It helps restore strength and function following injuries, supports the healing process, and reduces the risk of re-injury by gradually rebuilding muscle and joint stability.
Benefits for Older Adults
Combating Sarcopenia
Age-related muscle loss (sarcopenia) can significantly affect mobility and independence. Resistance training helps older adults maintain or even increase muscle mass and strength, improving their ability to perform daily tasks and reducing the risk of falls.
Enhancing Balance and Coordination
Strength training not only increases muscle mass but also improves neuromuscular coordination and balance. This is particularly important for older individuals, as better balance can prevent falls and related injuries.
Supporting Long-Term Health
The improvements in bone density, metabolic health, and overall physical function that come from resistance training contribute to a higher quality of life for older adults. Regular strength training can reduce the risk of chronic conditions such as osteoporosis, cardiovascular disease, and type 2 diabetes.
Metabolic and Cardiovascular Benefits
Increased Resting Metabolic Rate
By increasing lean muscle mass, resistance training elevates the resting metabolic rate, which means that your body burns more calories even when not exercising. This can help with weight management and long-term metabolic health.
Improved Blood Sugar Regulation
Enhanced insulin sensitivity from regular resistance training helps in better blood sugar management. This is particularly beneficial for preventing or managing type 2 diabetes and other metabolic disorders.
Better Lipid Profiles
Resistance training can lead to improvements in cholesterol levels, such as increasing HDL (good) cholesterol and reducing LDL (bad) cholesterol. These changes contribute to improved cardiovascular health and reduced risk of heart disease.
Versatility and Adaptability
Multiple Training Modalities
Resistance training is highly versatile. It can be performed using free weights, machines, resistance bands, or even bodyweight exercises. This adaptability makes it accessible to people of all ages and fitness levels, whether at home, in the gym, or as part of a rehabilitation program.
Tailored Programs for Specific Goals
Whether your goal is to build muscle, improve athletic performance, lose weight, or rehabilitate an injury, resistance training programs can be customized to meet your specific needs. This tailored approach ensures that everyone—from beginners to elite athletes—can benefit from resistance training.
Optimizing Training and Recovery
Progressive Overload
The principle of progressive overload—gradually increasing the resistance or volume over time—is essential for continuous improvement in strength and muscle growth. This method ensures that muscles are continually challenged, leading to sustained improvements.
Importance of Recovery
Adequate recovery is crucial for maximizing the benefits of resistance training. Incorporating proper warm-up routines, stretching, foam rolling, and ensuring quality sleep helps prevent overtraining and allows the body to repair and grow stronger.
Balancing Work and Rest
Integrating rest days and active recovery into your training schedule is essential. Recovery helps reduce muscle soreness, prevents injuries, and allows for consistent progress over time.
Nutritional Considerations
Supporting Muscle Growth and Recovery
A balanced diet rich in proteins, carbohydrates, and healthy fats is vital for resistance training. Protein is particularly important for muscle repair and synthesis, while carbohydrates provide the energy needed for intense workouts.
Timing of Nutrient Intake
Consuming a protein-rich meal or supplement after training can enhance muscle recovery. Additionally, proper hydration and electrolyte balance support overall performance and help prevent fatigue during workouts.
Supplements and Ergogenic Aids
Certain supplements, such as creatine, branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs), and vitamin D, can further support resistance training by enhancing muscle performance, improving recovery, and maintaining overall health.
Long-Term Health and Longevity
Preventing Chronic Diseases
The metabolic and cardiovascular improvements from resistance training contribute to the prevention of chronic diseases such as type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and osteoporosis. Regular strength training supports a healthier body composition and improved physiological function.
Maintaining Mobility and Independence
For all age groups, particularly older adults, resistance training helps maintain muscle mass and joint function. This preservation of physical capacity is key to sustaining an active lifestyle and long-term independence.
Enhancing Quality of Life
Beyond the physical and metabolic benefits, resistance training improves mental health, self-esteem, and overall quality of life. It provides a sense of achievement and empowerment, encouraging a more active, engaged lifestyle.
Conclusion
Resistance training offers a wealth of benefits that extend far beyond mere muscle growth. It improves physical strength, body composition, and bone density while enhancing metabolic health, cardiovascular function, and overall athletic performance. In addition, the mental and psychological benefits, such as reduced stress, improved mood, and increased self-confidence, make it an essential component of any well-rounded fitness program. Whether you are an athlete, a fitness enthusiast, or someone looking to improve your health and longevity, incorporating resistance training into your routine can lead to transformative results.